Architectural elements
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
A
[edit]-
Arcade, passage or walkway covered over by a succession of arches or vaults supported by columns.
-
Arch, opening in a building that is curved on top.
-
Arcosolium, arched recess used as a burial place in a catacomb.
-
Arris, the sharp edge formed by the intersection of two surfaces
-
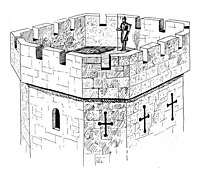
Arrowslit, or called Balistraria, thin vertical aperture in a fortification
-
Ashlar, dressed stone work of any type of stone.
-
Atlas, a support sculpted in the form of a man, which may take the place of a column, a pier or a pilaster
-
Atrium, a large open space, often several stories high and having a glazed roof and/or large windows
-
Attic, a space found directly below the pitched roof of a house
B
[edit]-
Ball flower, an architectural ornament in the form of a ball inserted in the cup of a flower
-
Baluster, a moulded shaft standing on a unifying footing and supporting the coping of a parapet or the handrail of a staircase.
-
Balcony, a platform projecting from the wall of a building, supported by columns or console brackets, and enclosed with a balustrade
-
Barrel vault, an architectural element formed by the extrusion of a single curve (or pair of curves, in the case of a pointed barrel vault) along a given distance
-
Battlement, a low wall around the top of a castle, or wall with gaps for shooting through
-
Bay, the distance between two supports of a vault or the unit of an opening and its framing on a façade
-
Bell chamber, the room in which the bells are housed; its walls are pierced by openings which allow the sound to escape.
(images) -
Blind arcade, an arcade that is composed of a series of arches that has no actual openings and that is applied to the surface of a wall as a decorative element
-
Blind arch, an arch found in the wall of a building which has been infilled with solid construction so it cannot serve as a passageway, door, or window
(images) -
Bossage, a stone in a building, left rough and projecting.
-
Bulkhead, an exterior entrance with doors to a cellar or basement.
C
[edit]-
Cable railings. Safety rails that use horizontal or vertical cables in place of spindles, glass, mesh etc. for infill.
-
Camber beam. A piece of timber cut archwise, or with an obtuse angle in the middle, commonly used in platforms, as church leads, and other occasions where long and strong beams are required.
D
[edit]E
[edit]-
Eaves can be of various materials.
F
[edit]-
Flying buttress, a specific form of buttressing mostly associated with Gothic church architecture. The purpose is to resist the lateral forces pushing a wall outwards by redirecting them to the ground. (images)
G
[edit]H
[edit]-
Hypogeum. An underground temple or tomb.
I
[edit]J
[edit]K
[edit]M
[edit]-
Matroneum. A gallery on the interior of a building, originally intended to accommodate women. In medieval churches matronea became purely architectonic elements, placed over the side aisles. In Early Gothic churches the matronea were one of the four elements which constituted the interior walls (arch, matroneum, triforium and clerestory). (images)
-
Mantel (mantelpiece, chimneypiece). A decorative surround of a fireplace, usually of wood or stone, sometimes of tile or iron; sometimes includes a mantleshelf and/or a decorative overmantel. The sides are jambs. (mantel images) (overmantel images)
P
[edit]-
Pergola. A garden feature forming a shaded walk or passageway of pillars that support cross-beams and a sturdy open lattice, upon which woody vines are trained.
-
Porch. A structure attached to a building, forming a covered entrance to a vestibule or doorway.
-
Portico. A porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls.
W
[edit]-
Wall anchor